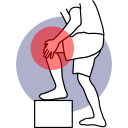
knee Joint
The knee joint is a complex structure that plays a crucial role in mobility. Here’s an overview of its key components:
• Femur: The thigh bone, which has two rounded ends (condyles) that form the upper part of the knee joint.
• Tibia: The shinbone, which bears most of the weight and forms the lower part of the knee joint.
• Fibula: A smaller bone located next to the tibia, providing stability.
• Patella: The kneecap, which protects the joint and improves leverage for the thigh muscles.
- Articular Cartilage: Smooth tissue covering the ends of the femur and tibia, allowing for smooth movement.
- Menisci: Two C-shaped cartilage structures (medial and lateral meniscus) that cushion and stabilize the knee.
• Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL): Provides stability by preventing forward movement of the tibia.
• Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL): Prevents the tibia from moving backward.
• Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL): Stabilizes the inner side of the knee.
• Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL): Stabilizes the outer side of the knee.
• Quadriceps Tendon: Connects the quadriceps muscle to the patella.
• Patellar Tendon: Connects the patella to the tibia.
• Quadriceps: Front thigh muscles that extend the knee.
• Hamstrings: Back thigh muscles that flex the knee.
• Calf Muscles: Assist in knee movement and stability.
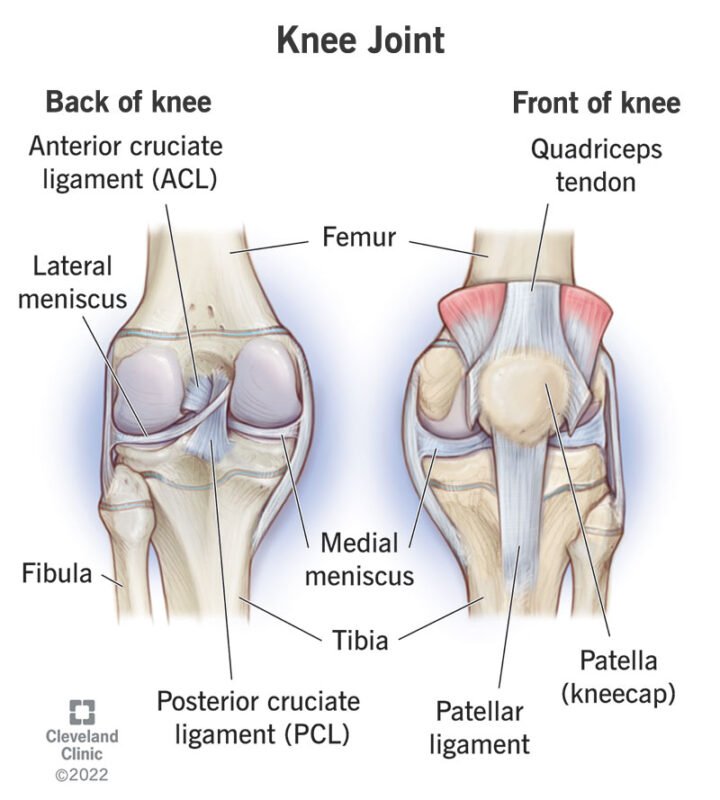
Knee pain can arise from various causes, including:
- Injuries: Sprains, strains, fractures, and tears (like ACL or meniscus tears) can lead to pain.
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage in the knee joint can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that leads to inflammation and pain in the joints.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the knee, often due to overuse.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (small fluid-filled sacs) that cushion the knee joint.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Pain around the kneecap often due to overuse, muscle imbalances, or misalignment.
Signs and symptoms of knee pain can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common ones include:
Signs and symptoms
- Pain: Varies from a dull ache to sharp pain, especially during movement or weight-bearing activities.
- Swelling: Inflammation can cause the knee to appear swollen or puffy.
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee, often worse after resting.
- Instability: A feeling that the knee might give out or buckle under weight.
- Popping or Clicking Sounds: Noises during movement, which might indicate structural issues.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Limited ability to fully extend or flex the knee.
- Tenderness: Sensitivity around the knee joint when touched.
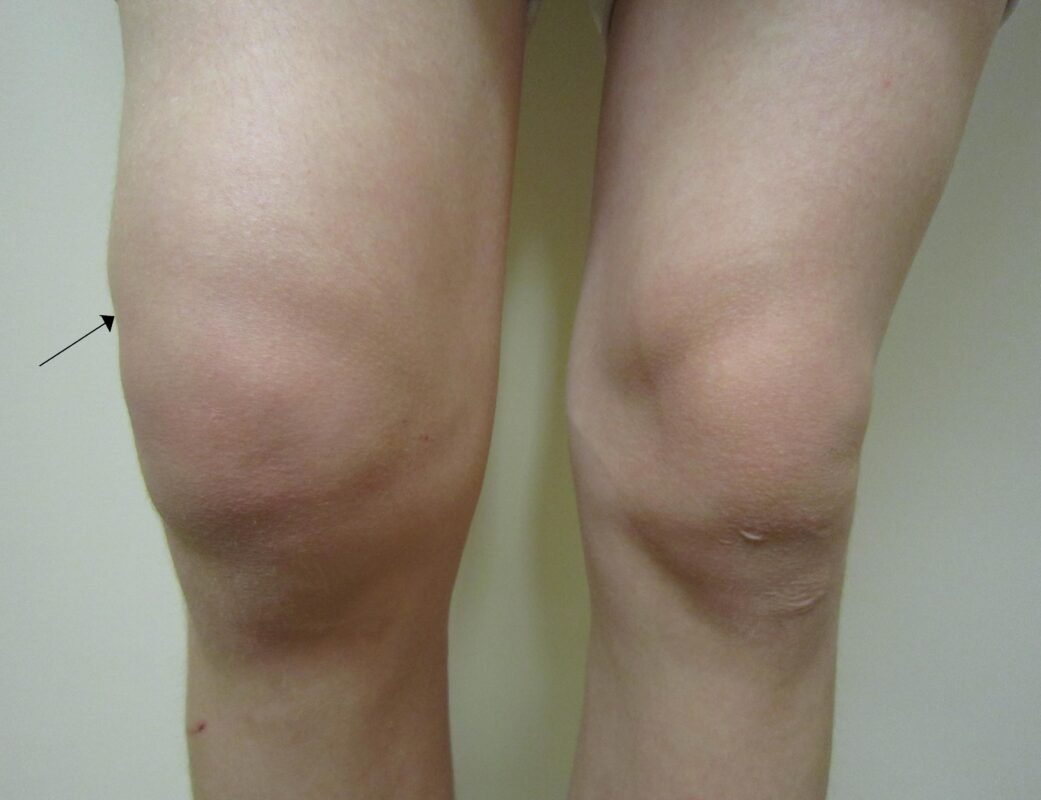
Knee joint pain can occur in several areas, including:
- Front of the knee: Often related to patellar issues, such as patellar tendinitis or chondromalacia (softening of the cartilage under the kneecap).
- Side of the knee: Pain here may indicate issues with the iliotibial band or ligament injuries, such as lateral collateral ligament (LCL) sprains.
- Back of the knee: This could be due to problems like Baker's cysts or hamstring injuries.
- Inside of the knee: Pain in this area may suggest medial meniscus tears or medial collateral ligament (MCL) injuries.
- Generalized pain: This can be a sign of arthritis or other systemic issues affecting the joint.
 +91 8248827895 |
+91 8248827895 |  absolutevitalhealth@gmail.com
absolutevitalhealth@gmail.com
 Joint Pain
Joint Pain